Stepper Library
The Stepper library allows you to connect stepper motors, which move in small individual steps that makes slow and precise movement easy.Download: Stepper is included with Arduino
Hardware Requirements
Stepper is compatible with all Teensy boards. Stepper can control unipolar or bipolar stepper motors. In this photo, Stepper is controlling a unipolar stepper motor salvaged from an old Teac 5¼ inch floppy disk drive.
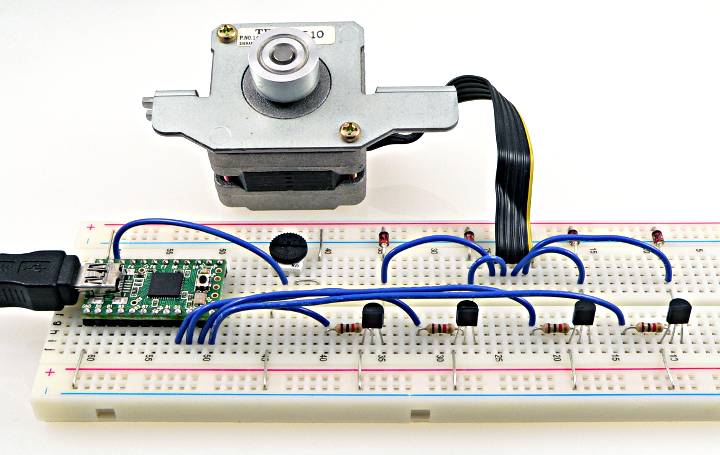
Small stepper motors designed for 5 volts may be able to run from power provided by USB. Larger motors will require separate power.
Basic Usage
Stepper mystepper(steps, pin1, pin2, pin3, pin4);Create an instance of the Stepper library for a unipolar type stepper motor. You will need to create an instance for each motor, giving each motor a unique name of your choice.
Stepper mystepper(steps, pin1, pin2);Create an instance of the Stepper library for a bipolar type stepper motor.
Movement Control
mystepper.setSpeed(rpm);Sets the speed, in rotations per minute.
mystepper.step(number);Move the motor 1 or more steps. The number can be positive or negative, to specify the direction of movement.
Example Program
This example is a slightly modified version of MotorKnob, which can be opened from the File -> Examples -> Stepper menu.
/* MotorKnob - slightly modified * * A stepper motor follows the turns of a potentiometer * (or other sensor) on analog input 0. */ #include <Stepper.h> // the number of steps on your motor #define STEPS 200 // create an instance of the stepper class, specifying // the number of steps of the motor and the pins it's // attached to Stepper stepper(STEPS, 7, 9, 8, 10); // the previous reading from the analog input long previous = STEPS / 2; void setup() { // set the speed of the motor to 30 RPMs stepper.setSpeed(30); } void loop() { // get the sensor value. This equation maps the // analogRead range to the number of steps, so the // motor nicely tracks a potentiometer's position long val = (long)analogRead(0) * STEPS / 1024; // move a number of steps equal to the change in the // sensor reading stepper.step(val - previous); // remember the previous value of the sensor previous = val; }
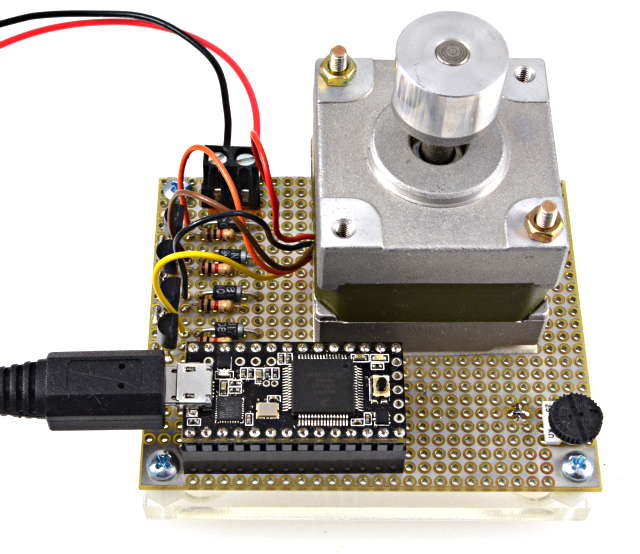
Unipolar Stepper Motors
TODO: info about unipolar type motorsTODO: schematic for circuit in photo above (2N3904 transistors, 1N4936 diodes, 1K resistors)
TODO: how to identify the common wire using a multimeter, and trial-error to get the windings sorted out
Bipolar Stepper Motors
TODO: info about bipolar type motorsTODO: suggested schematic using an "easy" H-bridge chip
TODO: how to identify each winding usine a multimeter